Continuity and Differentiability Class 12 Ncert Solutions Pdf
Practice Test - MCQs test series for Term 1 Exams
NCERT Solutions for Class 12-science Maths Chapter 5 - Continuity and Differentiability
Updated NCERT Textbook Solutions Coming Soon!
Chapter 5 - Continuity and Differentiability Exercise Ex. 5.1
Solution 1
The given function is f(x) = 5x - 3
At x = 0, f(0) = 5 × 0 - 3 = -3

Solution 2
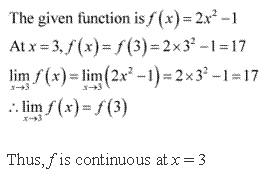
Solution 4

Solution 5


Solution 6


Solution 8


Solution 9

Solution 10


Solution 11

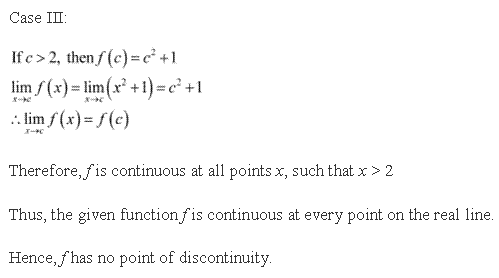
Solution 12



Thus, from the above observation, it can be concluded that x = 1 is the only point of discontinuity.
Solution 17

Solution 18

Solution 19

Solution 20
The given function is f(x) = x2 - sinx + 5
It is evident that f is defined at x = ∏

Solution 21


Solution 22



Therefore, cosecant is continuous except at x = np, n![]() Z
Z

Therefore, cotangent is continuous except at x = np, n![]() Z
Z
Solution 23


Solution 25


Solution 26
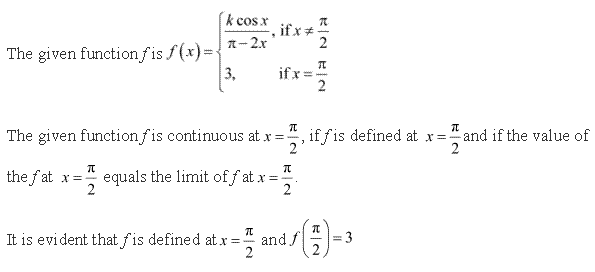
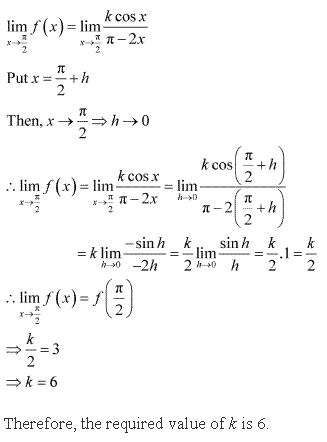
Solution 27

Solution 28
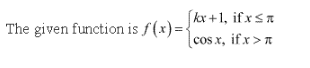
The given function f is continuous at x =![]() , if f is defined at x =
, if f is defined at x =![]() and if the value
and if the value
of f at x =![]() equals the limit of f at x =
equals the limit of f at x =![]()
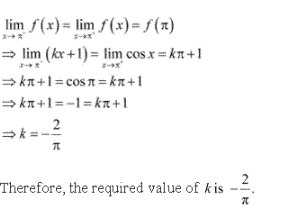
Solution 29

Solution 30


Solution 31


Chapter 5 - Continuity and Differentiability Exercise Ex. 5.2
Solution 1
Then, (v ο u)(x) = v(u(x)) = v(x2 + 5) = sin (x2 + 5) = f(x)

Solution 2

Solution 3

Solution 4
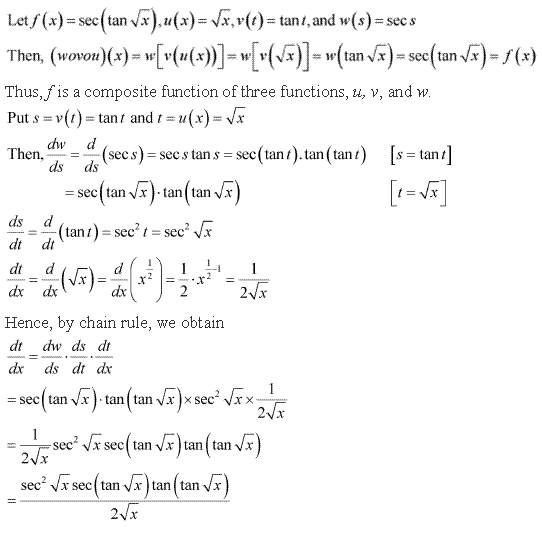
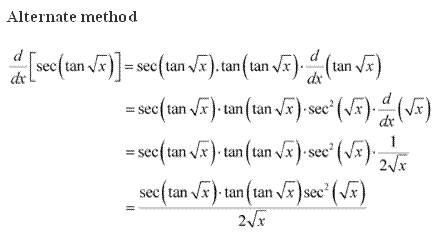
Solution 6
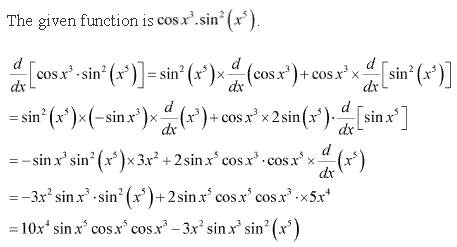
Solution 7
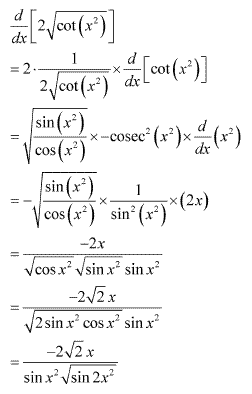
Solution 8
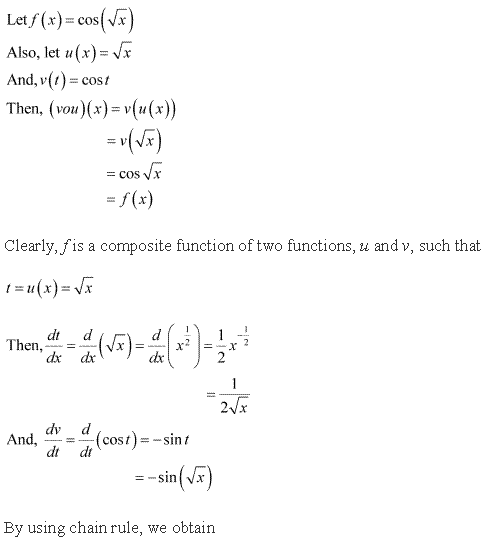
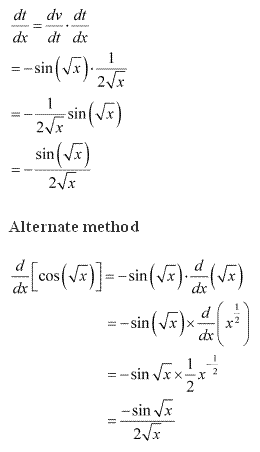
Solution 9
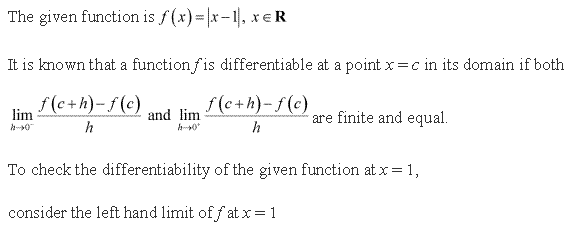

Solution 10


Chapter 5 - Continuity and Differentiability Exercise Ex. 5.3
Solution 1
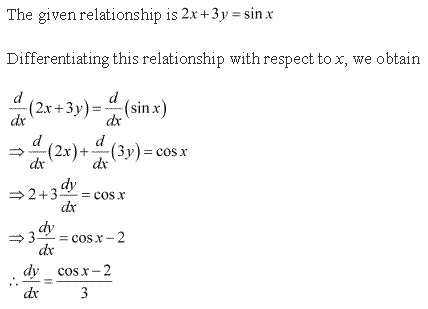
Solution 2
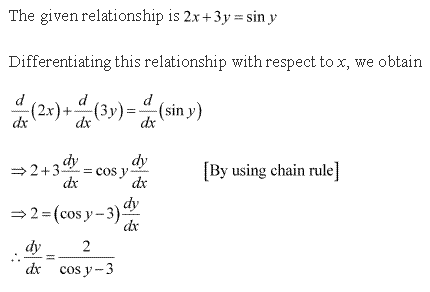
Solution 3
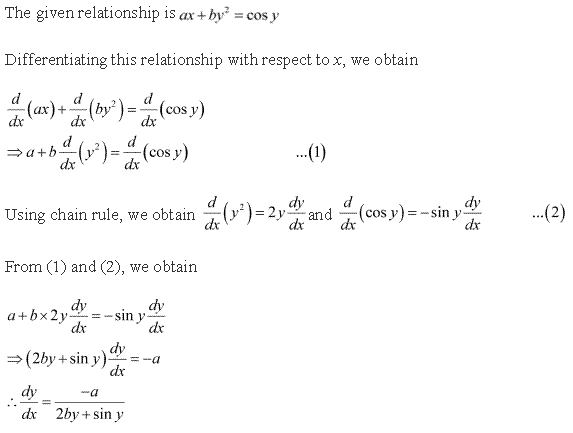
Solution 4
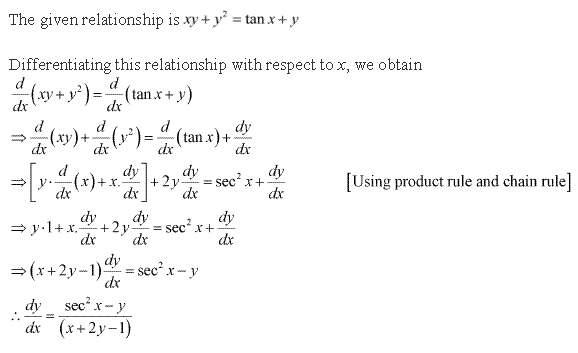
Solution 5
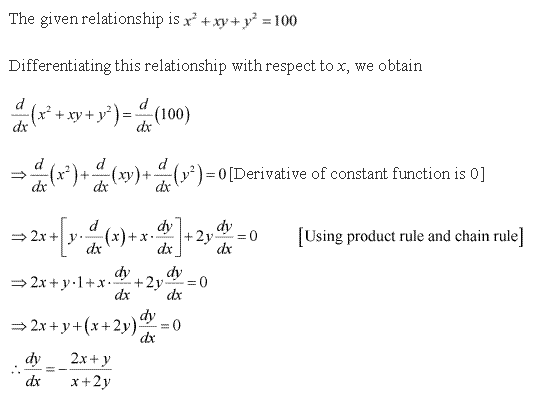
Solution 6
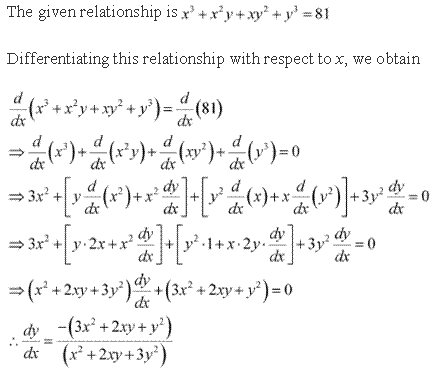
Solution 7

Solution 8

Solution 9

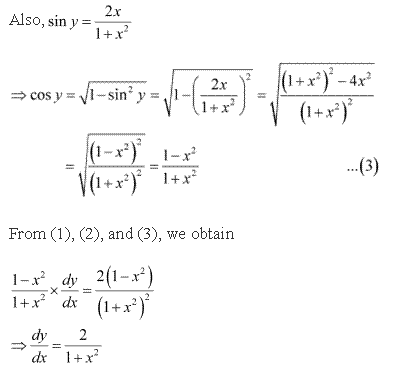
Solution 10
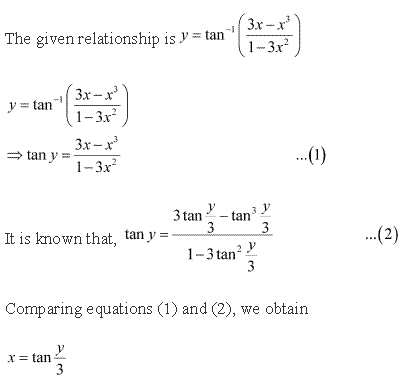
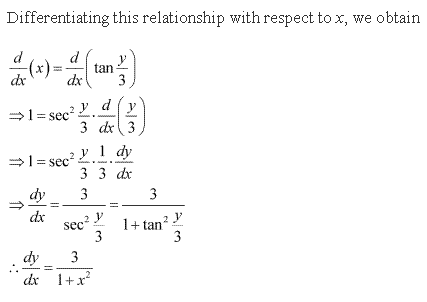
Solution 11

Solution 13
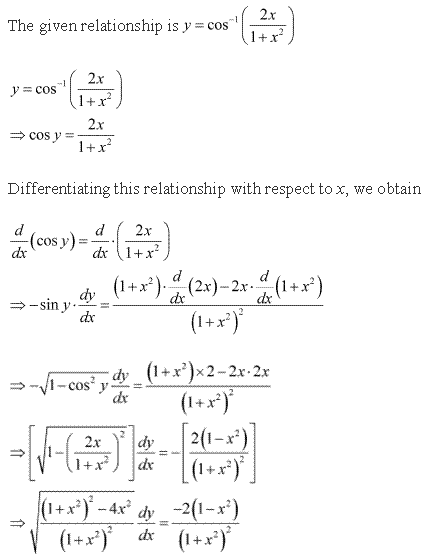
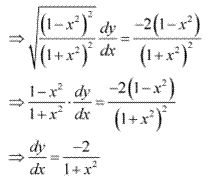
Solution 14
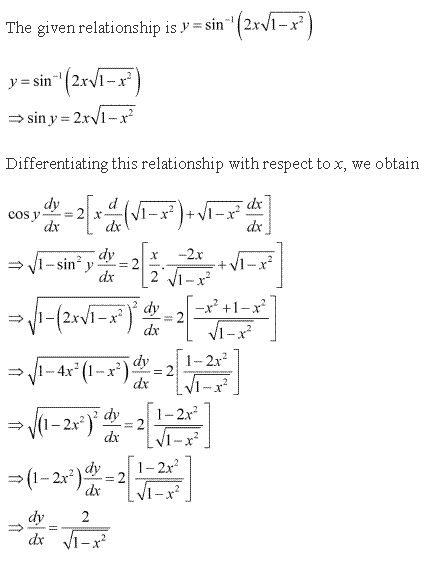
Solution 15
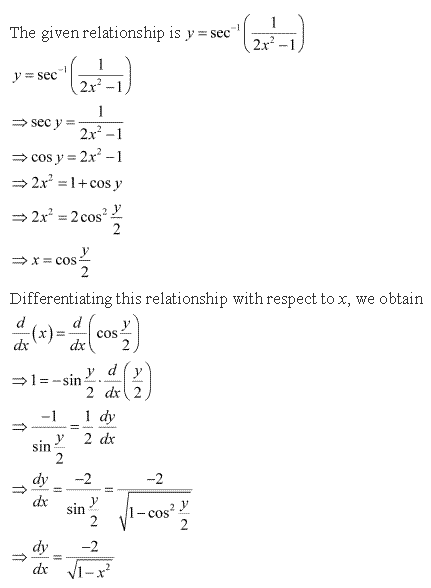
Chapter 5 - Continuity and Differentiability Exercise Ex. 5.4
Solution 1
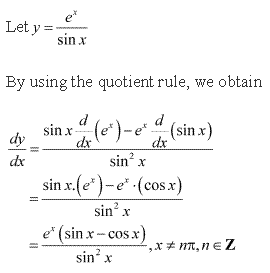
Solution 2
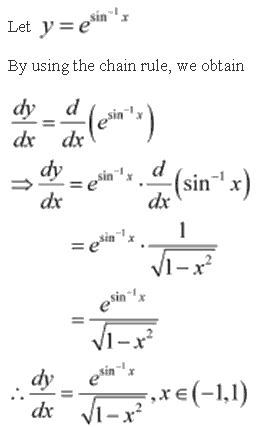
Solution 3
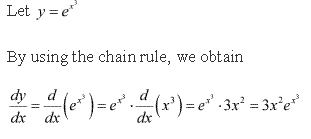
Solution 4
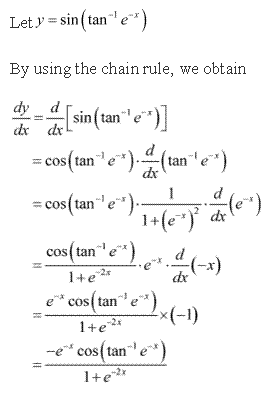
Solution 5
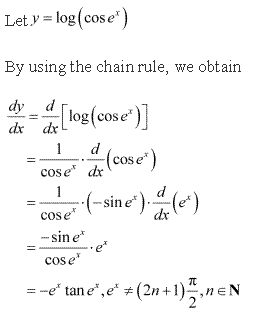
Solution 6
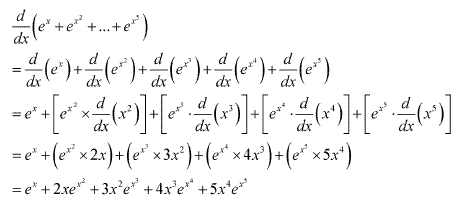
Solution 7
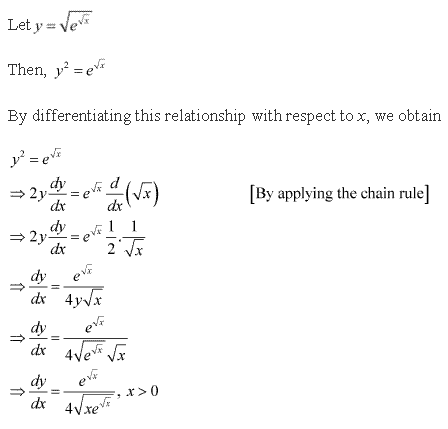
Solution 8
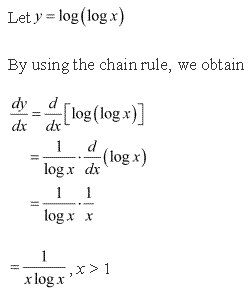
Solution 9
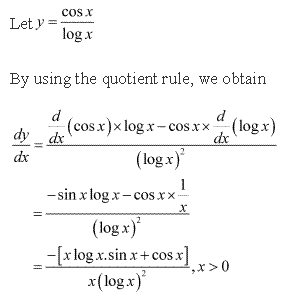
Solution 10
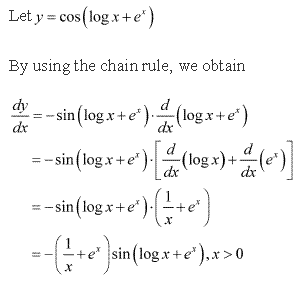
Chapter 5 - Continuity and Differentiability Exercise Ex. 5.5
Solution 1
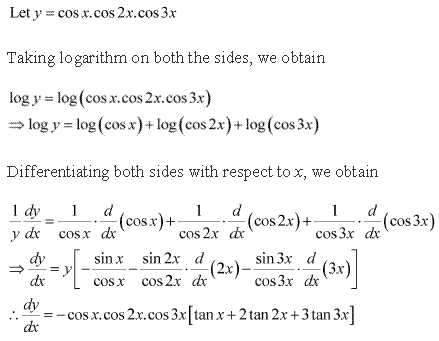
Solution 2

Solution 3

Solution 4


Solution 5
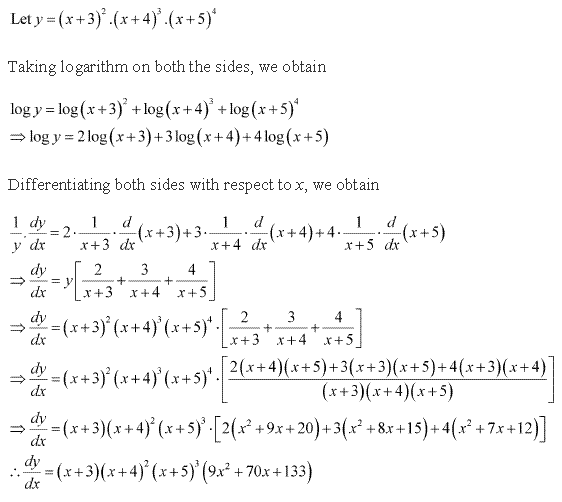
Solution 8
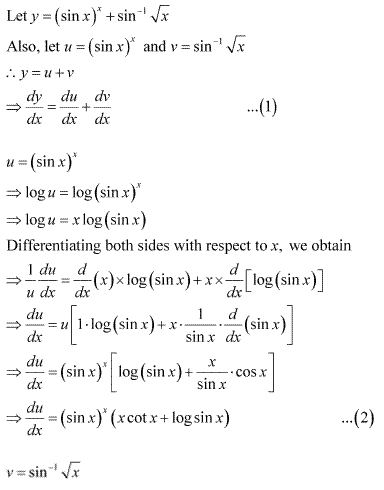
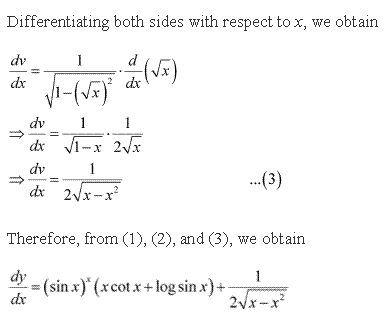
Solution 9

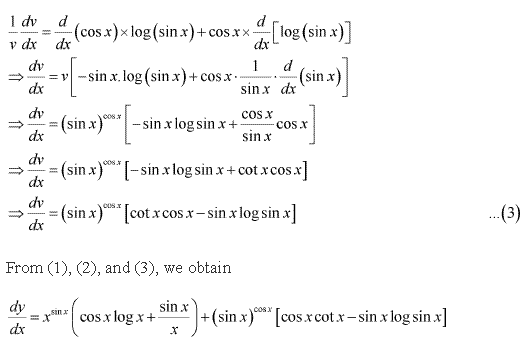
Solution 10


Solution 13

Solution 14
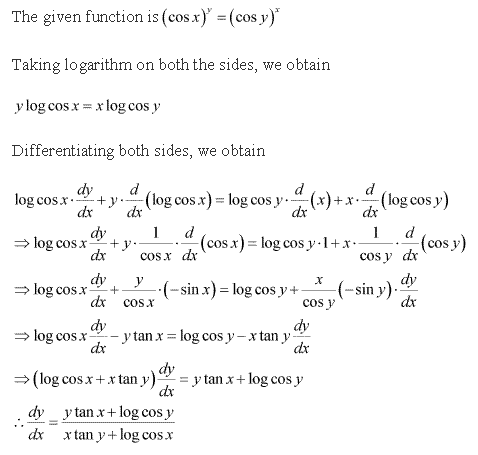
Solution 15
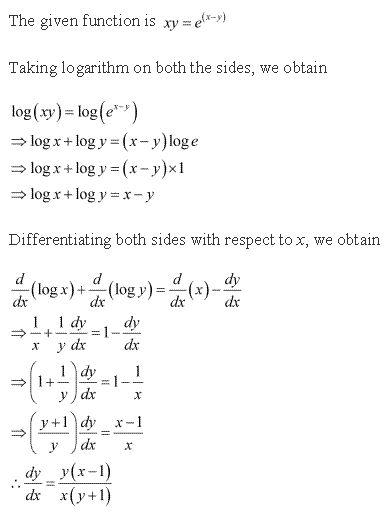
Solution 16
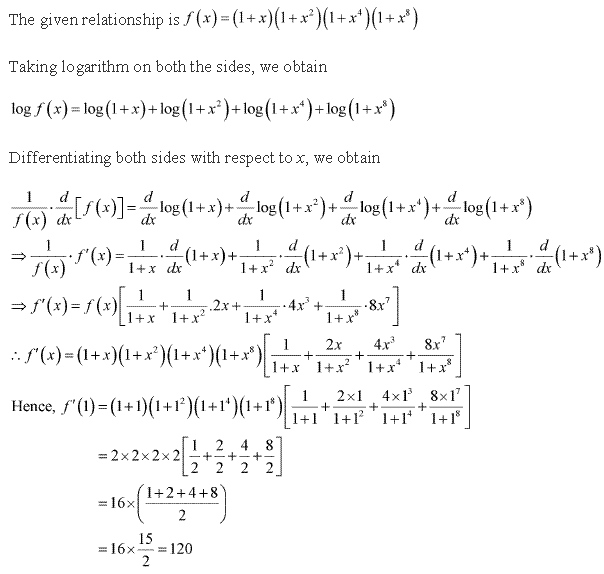
Solution 18

Chapter 5 - Continuity and Differentiability Exercise Ex. 5.6
Solution 1
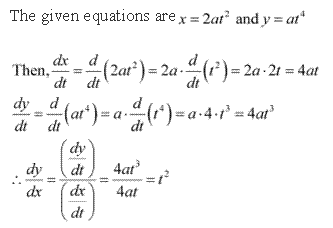
Solution 2
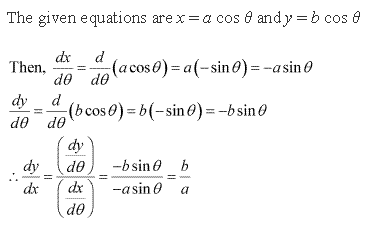
Solution 3
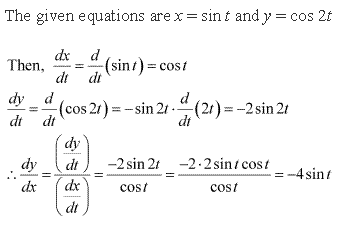
Solution 4
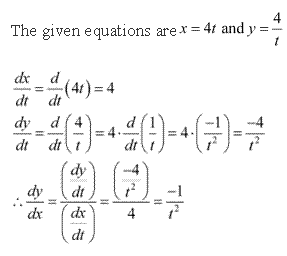
Solution 5
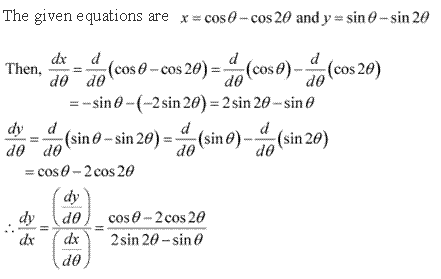
Solution 6
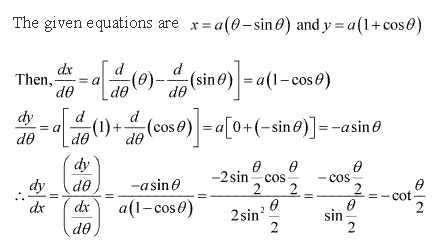
Solution 8
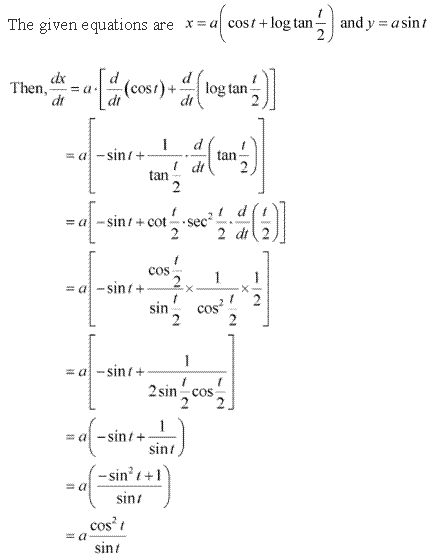
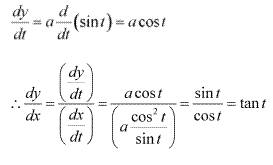
Solution 9
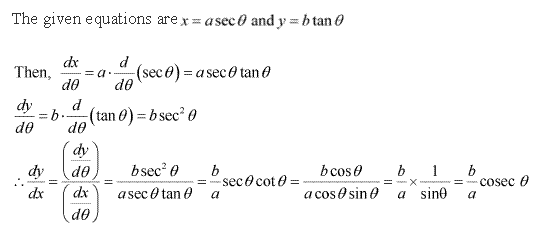
Solution 10
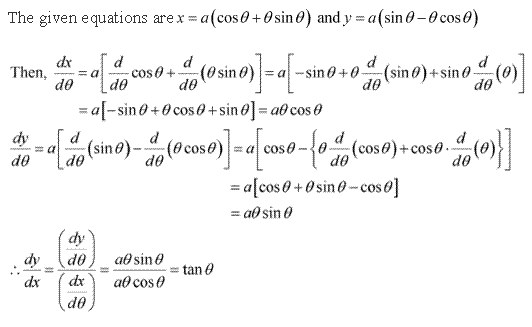
Solution 11
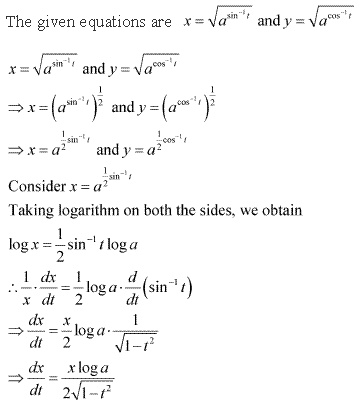
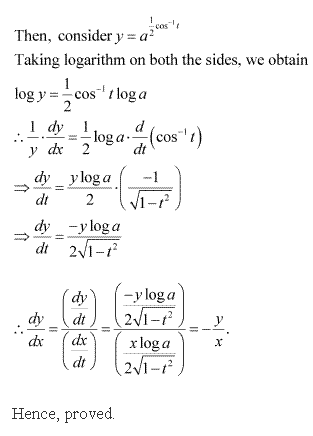
Chapter 5 - Continuity and Differentiability Exercise Ex. 5.7
Solution 1
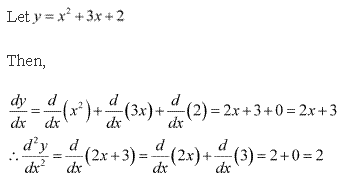
Solution 2
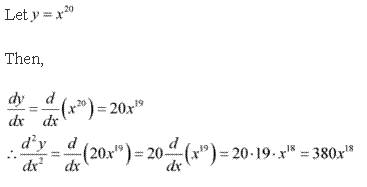
Solution 3
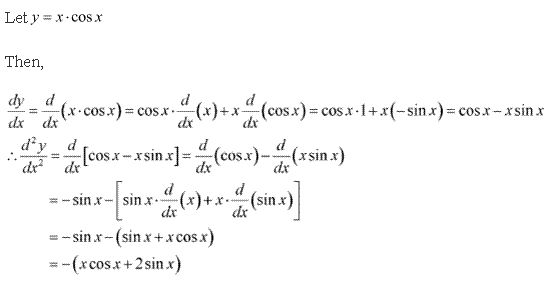
Solution 4
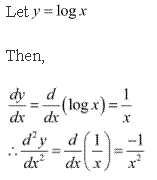
Solution 5

Solution 6
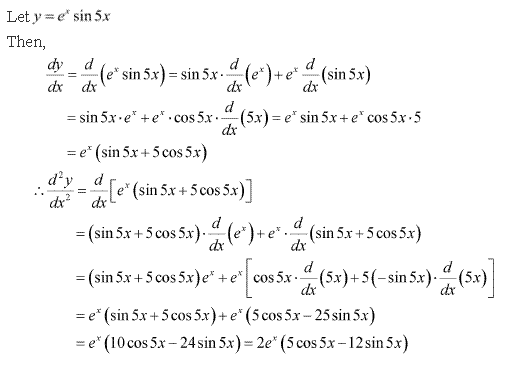
Solution 7
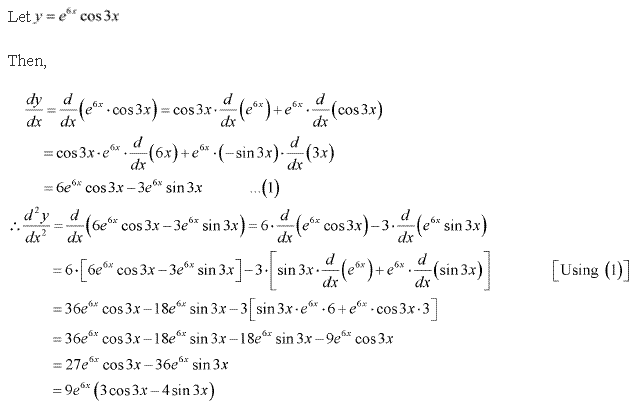
Solution 8
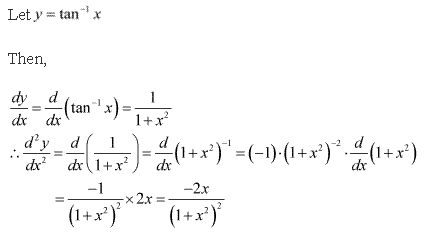
Solution 9
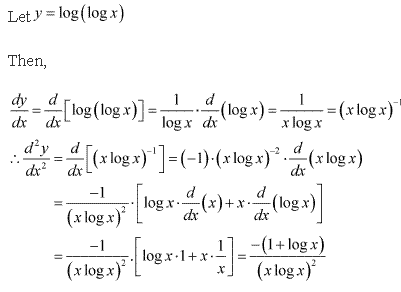
Solution 10

Solution 11
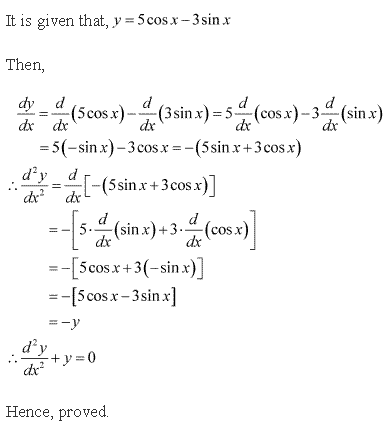
Solution 12
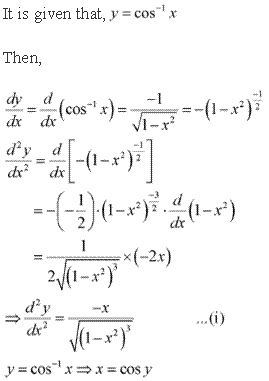
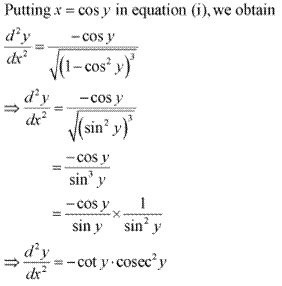
Solution 13
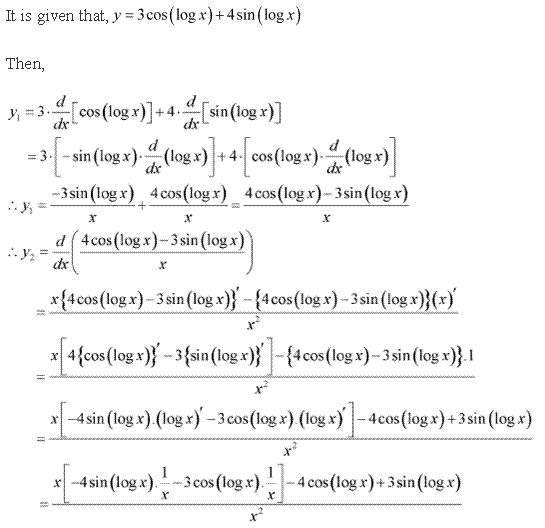
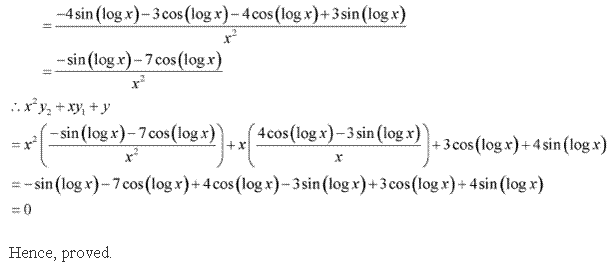
Solution 14
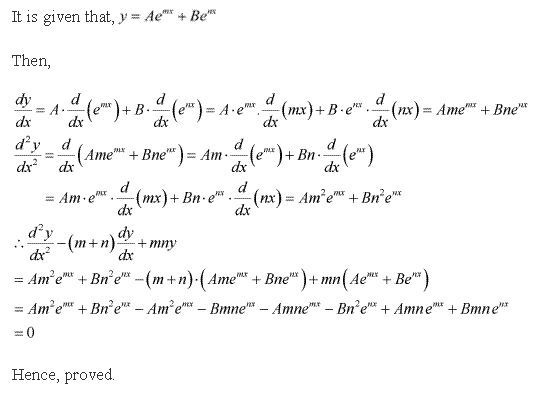
Solution 15
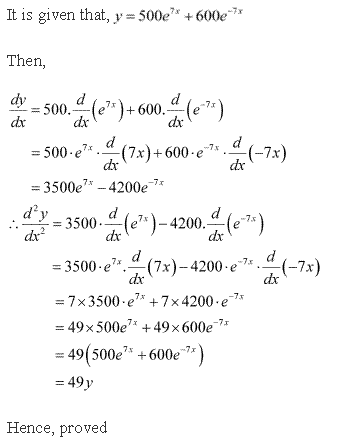
Solution 16

Solution 17

Chapter 5 - Continuity and Differentiability Exercise Ex. 5.8
Solution 1

Rolle's theorem states that there is a point c![]() (-4, -2) such that f'(c) = 0
(-4, -2) such that f'(c) = 0

Solution 2

then there exists some c![]() (a, b) such that f'(c) = 0
(a, b) such that f'(c) = 0

Let n be an integer such that n![]() (5, 9).
(5, 9).

Let n be an integer such that n ![]() (-2, 2).
(-2, 2).

Solution 3

Therefore, by the Mean Value Theorem, there exists c![]() (-5, 5) such that
(-5, 5) such that

Solution 4

Mean Value Theorem states that there is a point c![]() (1, 4) such that f'(c) = 1
(1, 4) such that f'(c) = 1

Solution 5

Chapter 5 - Continuity and Differentiability Exercise Misc. Ex.
Solution 1
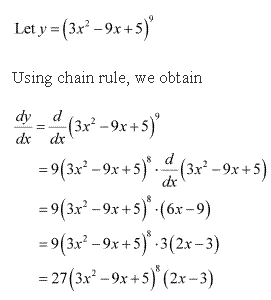
Solution 2
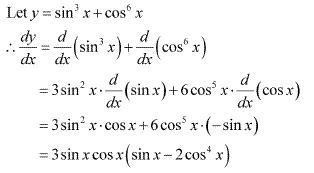
Solution 3

Solution 4
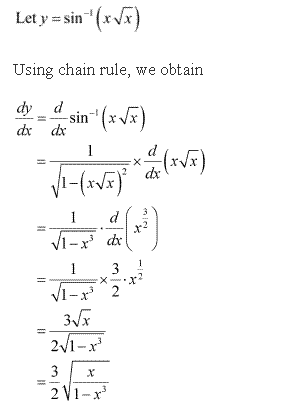
Solution 5
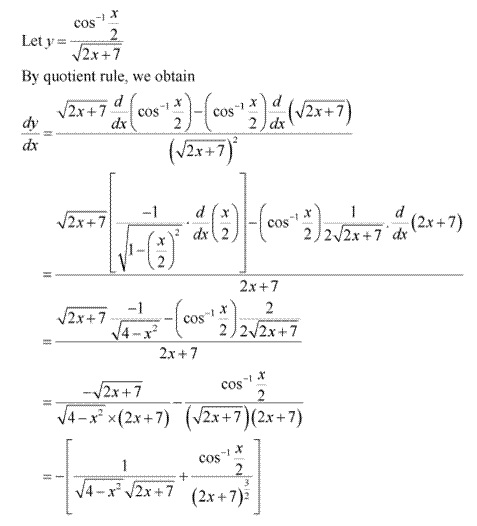
Solution 6
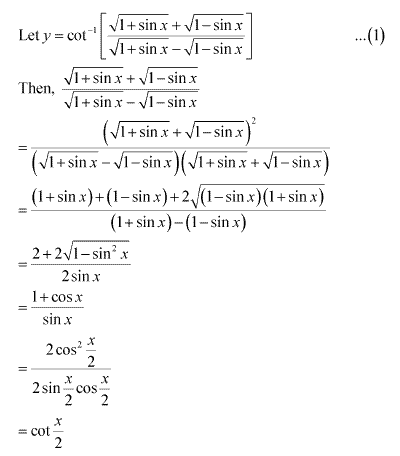
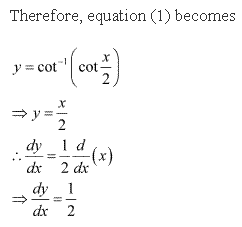
Solution 7

Solution 8
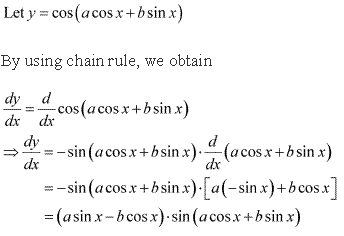
Solution 9

where sin x > cosx
Solution 11


Solution 12
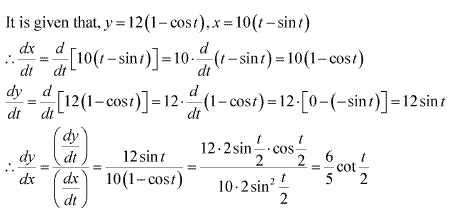
Solution 13
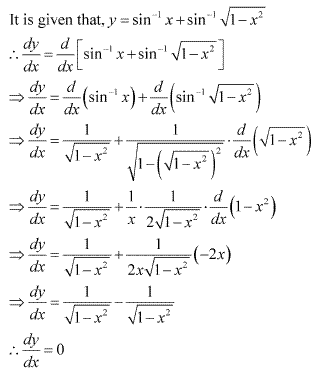
Solution 14

Solution 16
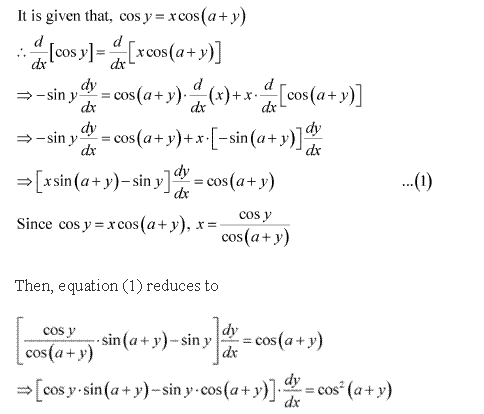

Solution 17
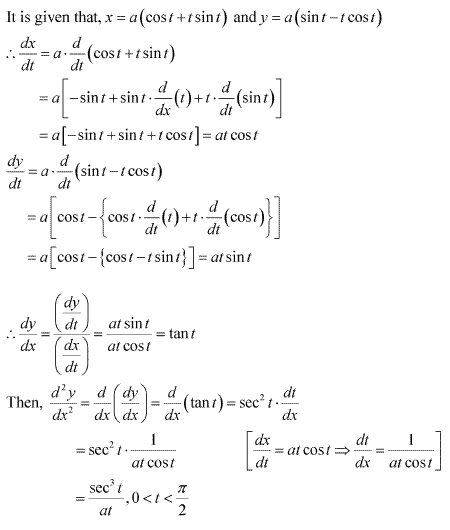
Solution 18
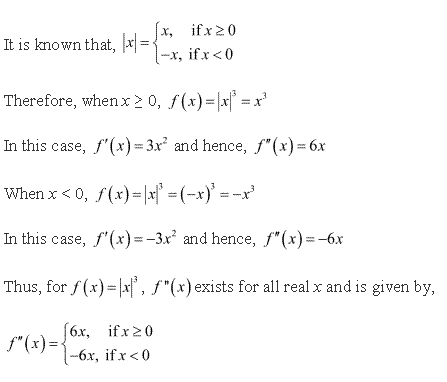
Solution 19
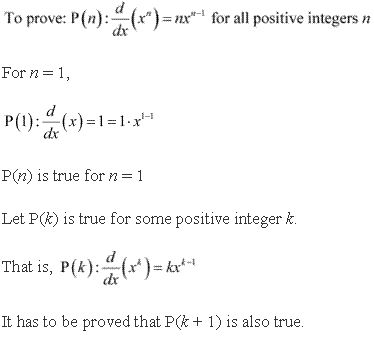
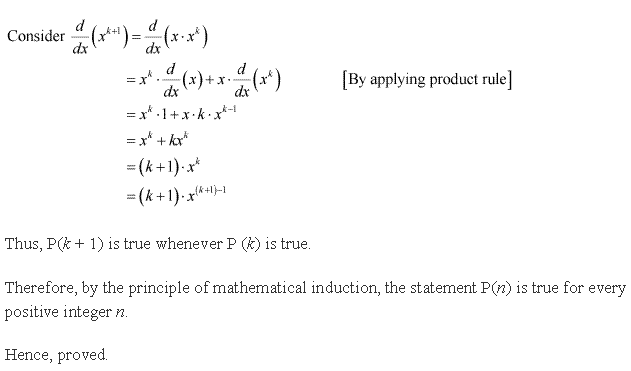
Solution 20
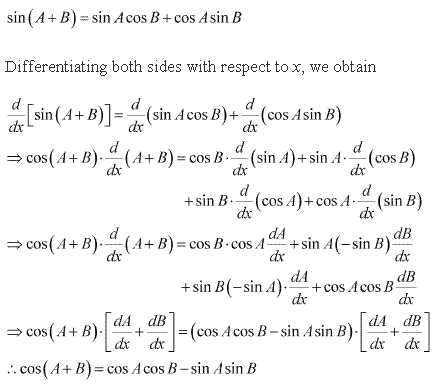
Solution 21
Yes.
Consider the function f(x)=|x-1|+|x-2|
Since we know that the modulus function is continuous everywhere, so there sum is also continuous
Therefore, function f is continuous everywhere
Now, let us check the differentiability of f(x) at x=1,2
At x=1
LHD = ![]()
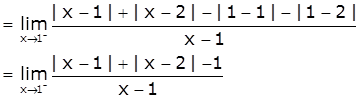
[Take x=1-h, h>0 such that h → 0 as x → 1-]
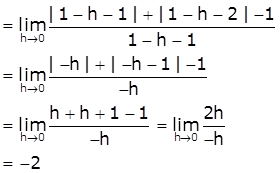
Now,
RHD = ![]()
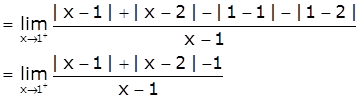
[Take x=1+h, h>0 such that h → 0 as x → 1+]
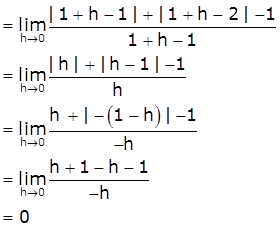
≠ LHD
Therefore, f is not differentiable at x=1.
At x=2
LHD = ![]()
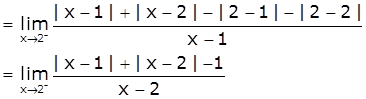
[Take x=2-h, h>0 such that h → 0 as x → 2-]
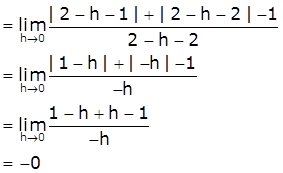
Now,
RHD = ![]()
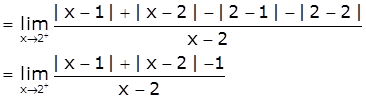
[Take x=2+h, h>0 such that h → 0 as x → 2+]
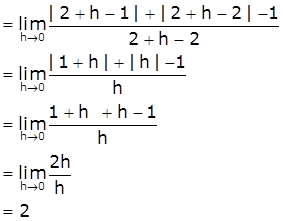
≠ LHD
Therefore, f is not differentiable at x=2.
Hence, f is not differentiable at exactly two points.
Solution 22
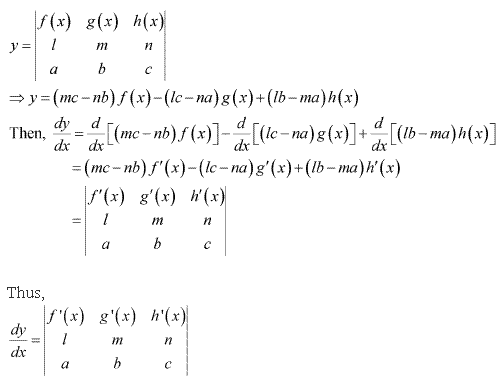
Solution 23

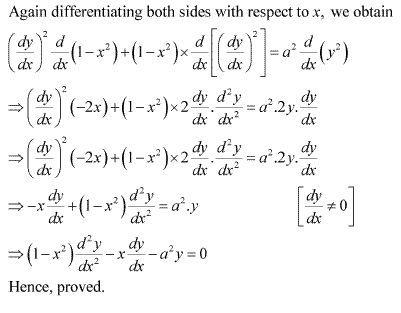
Continuity and Differentiability Class 12 Ncert Solutions Pdf
Source: https://www.topperlearning.com/ncert-solutions/cbse-class-12-science-mathematics/mathematics-xii/continuity-and-differentiability
0 Response to "Continuity and Differentiability Class 12 Ncert Solutions Pdf"
Post a Comment